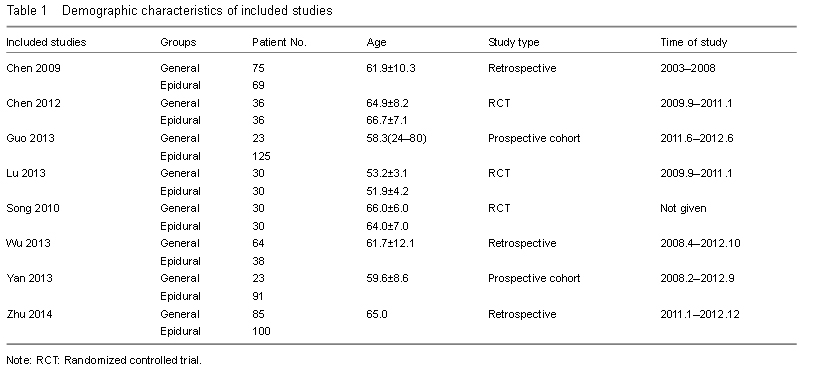
DVT is caused by the abnormal coagulation of blood in the deep vein. DVT often appears in lower extremities, and is one of the most serious complications after TKA. In most cases, DVT could cause swelling and pain of the lower extremities, and when the thrombus moves to lung and causes pulmonary embolism, it may end up with sudden death of the patient. With the application of anticoagulation drugs, the incidence of DVT has been dropped to 42% from the original 88% without any anticoagulants. Statistically, 0.2% of those patients developed pulmonary thromboembolism and resulted in sudden death[14-15]. More than 300 thousand patients died of pulmonary thromboembolism each year[16]. The prevention of thromboembolic disease is one of the most important points in preventing mortality after TKA.
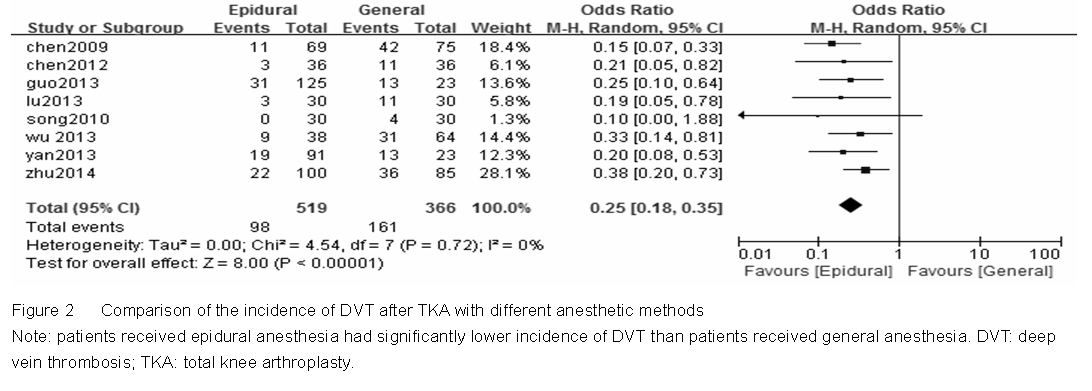
Plenty of studies concern the risk factors of DVT after TKA. According to the current literature, the high risk factors of DVT formation after TKA include old age, female, overweight and application of bone cement during the surgery[17]. In the current meta-analysis, patients with epidural anesthesia had significantly less DVT than patients who underwent TKA with general anesthesia. This result is in accordance with some other studies[18-19].
A number of reasons could be the causes of this effect. Epidural anesthesia has less effect on the blood coagulation than general anesthesia, drives more volume flow to the lower limbs and reduces the surgical stress response in the patient[20-21]. Epidural anesthesia can deactivate sympathetic nerves, dilate the blood vessels and increase the blood flow of the lower limb, decrease the secretion of catecholamine[22-23]. Moreover, patients with epidural anesthesia can walk shortly after the surgery, and then lower the incidence of DVT.
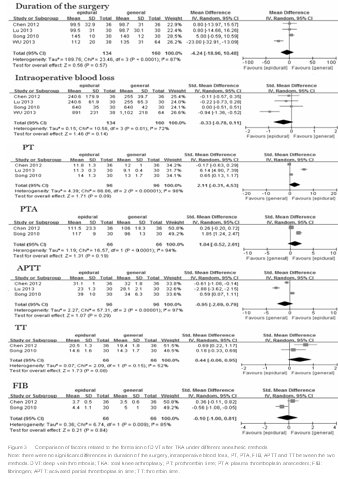
Although there were no significant differences between the two groups concerning factors that could affect the incidence of DVT formation after the surgery, such as duration of the surgery, intraoperative blood loss, PT, PTA, FIB, APTT and TT, it is possibly the bias that was caused by the sample size included in those meta-analysis.
It can be concluded from the current study that, continuous epidural anesthesia can significantly reduce the incidence of DVT if it replaces general anesthesia during TKA. This alteration should be considered in patients with high risk of forming thromboembolism such as varicose veins, malignancy, smoking, old age and the use of oral oestrogens[19]. We believe it is also possible that the incidence of DVT can be significantly lowered if general anesthesia is replaced by epidural anesthesia in patients with severe fractures of the lower extremity.
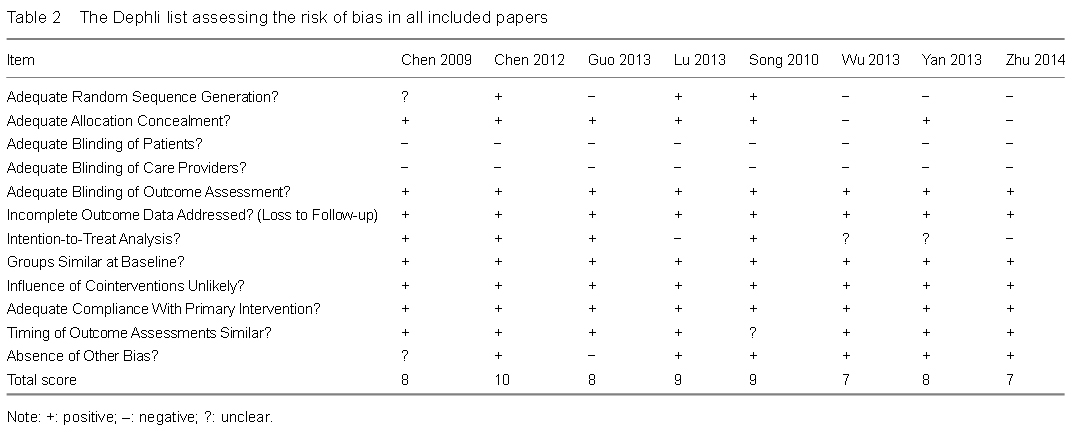
To our knowledge, the current meta-analysis is so far the study with the largest sample size. Although most of the studies included were published in Chinese language, the quality of those studies was tested by the Dephli list and proved to be qualified enough to be included in the meta-analysis. Moreover, the results driven from these studies can still serve as high grade evidence that can guide future clinical practice.
Results of this meta-analysis reveal that the ratio of DVT formation can be significantly (P < 0.01) reduced if general anesthesia can be replaced by epidural anesthesia in patients undergoing TKA.
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:
人工关节;骨植入物;
脊柱;
骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;
组织工程